
The United States recovered parts of the submarine in July 1974 from a depth around 5 km, in an operation named Project Azorian. The entire crew of 98 was lost and the vessel sank with three ballistic nuclear missiles as well as two nuclear torpedoes. On March 8, 1968, 1,560 nautical miles (2,890 km) northwest of Oahu in the Pacific Ocean, the Golf II-class submarine K-129 sank due to an explosion brought on by unknown cause, the accident being registered by the SOSUS network. Several views of a Project 629A (Golf II) ballistic missile submarine Project Azorian In 1959, the project technology was sold to China, which built a single modified example in 1966, which is still in service. It was described as having four missile launch silos in the sail, and is generally thought to refer to a repowered Golf II-class vessel. In that report, North Korean defector Kim Heung-kwang said a 3,500-ton, nuclear-powered submarine, one of a pair, was due for launch before 2018. Īn organization of defectors from North Korea, named In-Kook Yantai, published a report in 2016 entitled "North Korea's Nuclear and WMD Assessment". According to some sources, the North Koreans were attempting to get these boats back into service. In 1993, 10 were sold to North Korea for scrap. In later years, a few were converted to test new missiles and others had different conversions.Īll boats had left Soviet service by 1990.
#Gold submarine drawing upgrade#
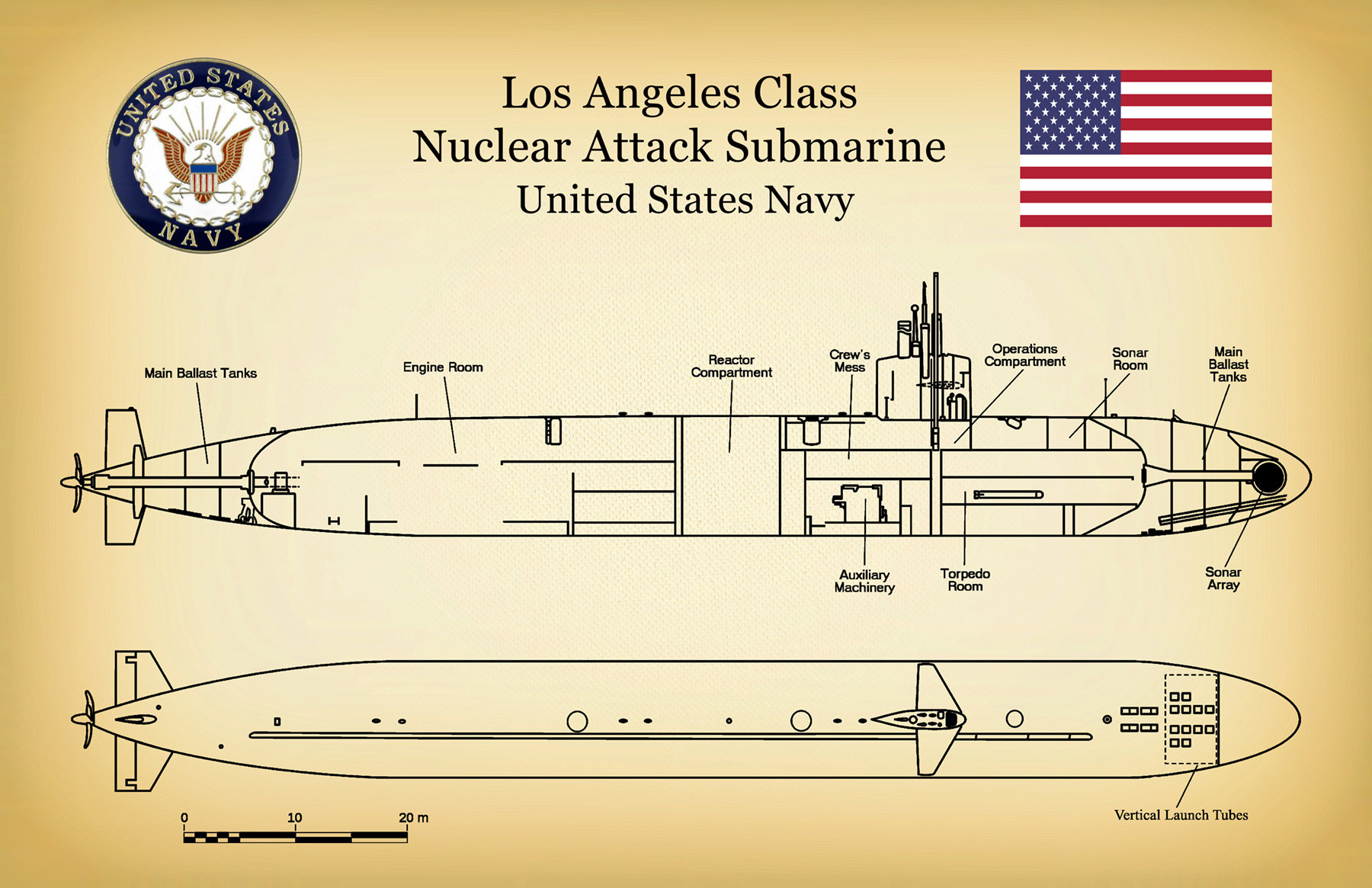
The major change was the upgrade of the missile system to carry R-21 missiles, which could be launched from inside their tubes with the submarine submerged and increased speed. Fourteen were extensively modified in 1966–1972 and became known as 629A by the Soviet Navy and "Golf II" by NATO (the original version having been designated "Golf I"). The boats were built at two shipyards - 16 in Severodvinsk and 7 in Komsomolsk-na-Amure in the Far East. The first boats were commissioned in 1958 and the last in 1962. Only the first three boats were equipped with these the remaining ones were equipped with the longer-range R-13 missiles. They could only be fired with the submarine surfaced and the missile raised above the sail, but the submarine could be underway at the time. These were carried in three silos fitted in the rear of the large sail behind the bridge. The submarine was originally designed to carry three R-11FM ballistic missiles with a range around 150 km. The design task was assigned to OKB-16, one of the two predecessors (the other being SKB-143) of the Malakhit Marine Engineering Bureau, which would eventually become one of the three Soviet/Russian submarine design centers, along with the Rubin Design Bureau and the Lazurit Central Design Bureau. Project 629 was started in the mid-1950s along with the D-2 missile launch system, which it was to carry, and was based on the Foxtrot-class submarine. According to some sources, at least one Golf-class submarine was operated by China, to test new submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs). All boats of this class had left Soviet service by 1990, and have since been disposed of. Project 629 ( Russian: проект–629, Projekt-629), also known by the NATO reporting name Golf, was a class of diesel-electric ballistic missile submarines that served in the Soviet Navy. 1966 onwards 629A upgrade D-4 launch system with R-21 missiles.Remaining boats D-2 launch system with R-13 missiles.3 × Project 629 boats D-1 launch system with R-11FM missiles.Surface - 17 kn, 9.500 nmi/5 kn submerged - 12kn


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
